Understand the concept of GLOBAL WARMING AND GREENHOUSE GASES 12 with UPSC CSE GS course curated by Deepak Singh on Unacademy The Environment & Ecology course is delivered in HindiGreenhouse Gas Removals (GGRs) are essential for limiting greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere and for achieving global temperature targets GGRs can be used to compensate for emissions from activities that are likely to remain very difficult to abate, such as aviation and agriculture, and can be used to bring down future atmospheric CO 2 concentrations if the target The Agreement aims to limit the greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed C or even 150C above preindustrial levels Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate S 1000 billion a year from to help developing countries to cope

Upsc Cds Exam Feb 08 Thorpes Education
Greenhouse gases list upsc
Greenhouse gases list upsc- Greenhouse gases apply a thermal FORCING Forcing is an appropriate word to use since greenhouse gases do not instantaneously warm the atmosphere (and indirectly the surface) The apply a constant forcing that results in a shift in the atmospheric (and indirectly the surface) temperature towards a higher equilibrium value There's nothing "emotively biased"2 days ago # The three greenhouse gases of greatest concern are carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere to keep the Earth warm, which is known as the greenhouse




Immediate Action Required An Open Letter To The Unfccc Secretariat Architecture 30
Greenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2 Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming one Methane, a powerful greenhouse gas which remains in the atmosphere for less than a decade, was 260% of preindustrial levels in 19 at 1 877There are a group of gases that are responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous dioxide, water vapor, and fluorinated gases They have different chemical properties and can gradually increase or decrease from the atmosphere through different processesThe one process that is most pressing at the moment (and has been for the past
Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent theIn simple terms, gases that trap heat in the earth's atmosphere are known as Greenhouse Gases, abbreviated as GHGs Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, Nitrous Oxide, Aerosols Share of Global GHG Emissions 15% A jet airliner leaves condensation trails in the sky The trails are formed by soot and water vapor from the plane engines which burn kerosene Aircraft emissions of water vapor, nitrous oxides, aerosols and CO2 at altitude could be two to four times stronger than
The earth has many gases that create a greenhouse effect by absorbing the heat of the sun, regulating the temperature from getting too cold But industrialisation and urbanisation has led to increased production of these greenhouse gases leading to a rise in the temperature of the earth Countries all over the globe came together in 1992 at the UNFCCC (UN FrameworkScientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping Longlived gases that remain semipermanently in the atmosphere and do not respondData can be displayed for individual Parties or groups of Parties, for different greenhouse gases or for their sum, and in varying degrees of detail To find the exact GHG data required, the user is advised to consult the following table where typical user requirements are mapped against the data availability on this site Latest UNFCCC publications with GHG data The latest UNFCCC
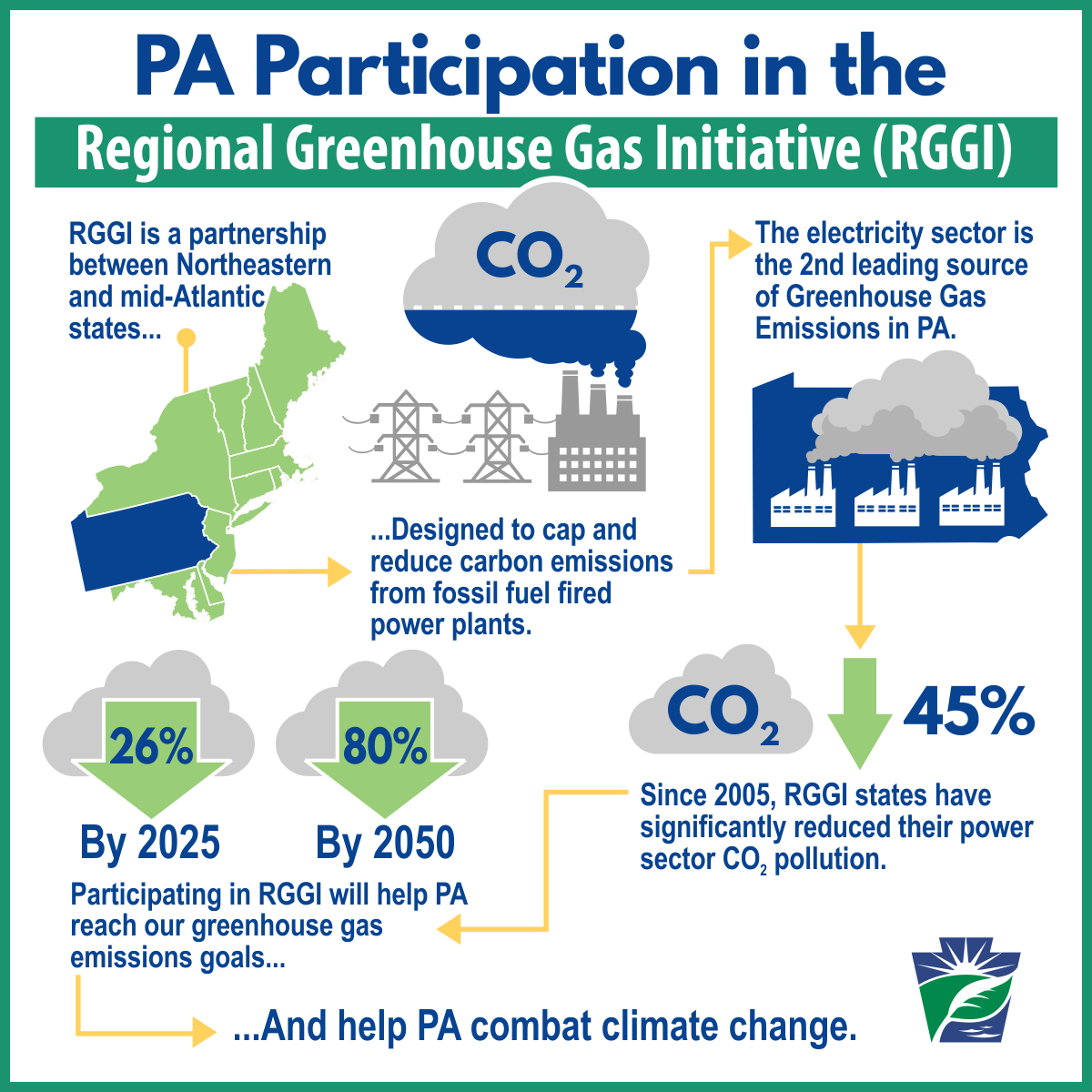



Rggi




Arrange The Following Greenhouse Gases According To Their Global Warming Potential Gwp In Ascending Order 1 Methane 2 Carbon Dioxide 3 Nitrous Oxide Select The Correct Answer Using The Code Given Below Forumias Blog
Species Chemical formula Lifetime (years) Global Warming Potential (Time Horizon) years 100 years 500 years Carbon dioxide CO 2 variable § 1 1 1 Methane *Greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), and carbon tetrachloride (CCI4) continue to increase because of human activities While the growth rates of most of these gases have been steady or increasing over the past decade, that of CH4 and some of the halocarbons has been decreasing The rateUPSC Prelims Answer Key;
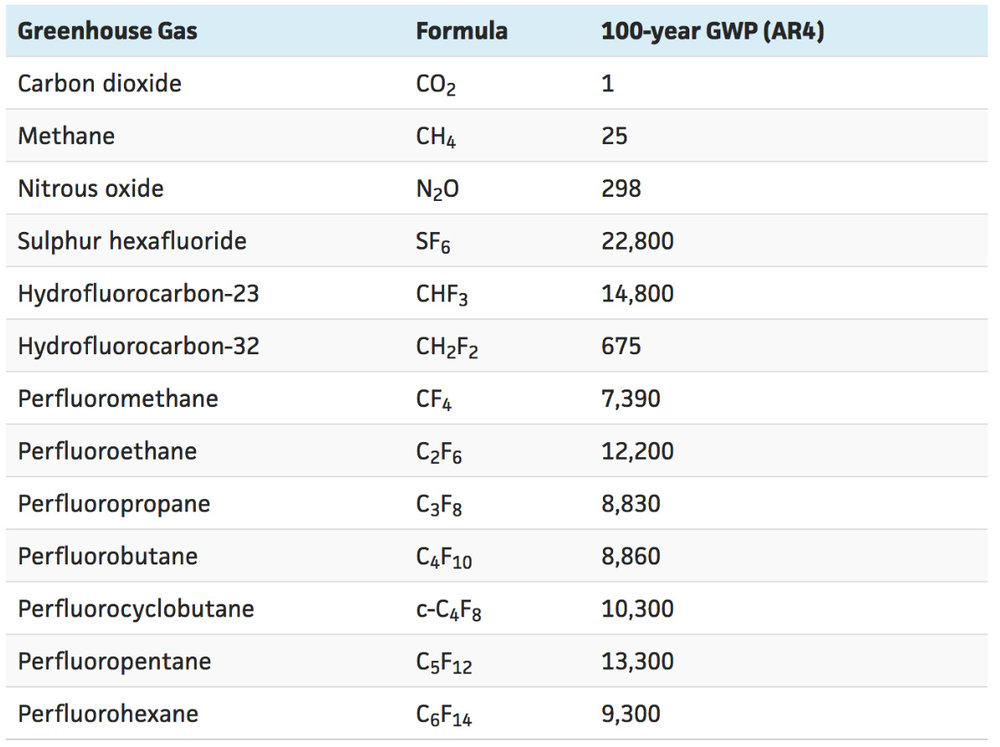



Climate Change Global Overview The Conscious Challenge




What Is Greenhouse Effect Burning Issues Free Pdf Download
Greenhouse gases hit new high Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere hit a new record in 18, exceeding the average yearly increase of the last decade and reinforcing Understand the concept of GLOBAL WARMING AND GREENHOUSE GASES 5 with UPSC CSE GS course curated by Deepak Singh on Unacademy The Environment & Ecology course is delivered in HindiUPSC Prelims Answer Key;




Unfccc 1992 Conference Of Parties Purpose Upsc Notes




Upsc Cds Exam Feb 08 Thorpes Education
HINT Anthropogenic is an adjective that may refer to pertaining to anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity The energy sector in India is responsible for 71% of country's total greenhouse gas emissions (GHG's), a report from India to the United Nations on climate change has revealed The 'Biennial Update Report' (BUR) was submitted to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change as part of India's responsibility to report the progress made on its promises to fight climate The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming



Which Books Should We Read For Environment And Ecology Syllabus Of Upsc Prelims And Mains Exams Quora




A History Of Climate Change Negotiations Civilsdaily
Q Which one of the following greenhouse gases is the largest single contributor to anthropogenic radiative forcing?The Climate Act calls for a 49% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 30, compared to 1990 levels, and a 95% reduction by 50 The National Climate Agreement contains agreements with the sectors on what they will do to help achieve these climate goals The participating sectors are electricity, industry, built environment, traffic and transport, and agriculture and land useTo cultivate the logical elimination 5050 skill, You must have strong foundation in environment So avoid the Baniyaagiri that why




Upsyyy Ias Books Syllabus Book Lists
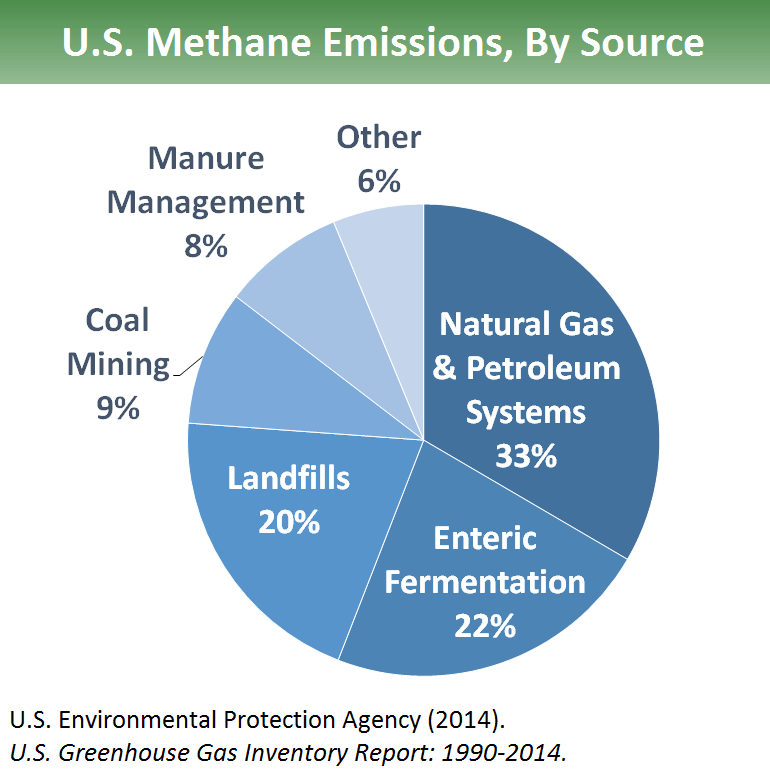



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases Greenhouse gases are not aCurrent Affairs Module (Prelims 21) Current Affairs Test Series (Prelims 21) Mains; The research and consulting firm, Rhodium Group, has released a report on Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Key Findings of the report Global Greenhouse gas emissions including emissions of all six Kyoto gases have reached 52 gigatons of CO2equivalent in 19 This is an 114% increase over the past decade The six main gases under Kyoto




Ias Preparation Simplified Like Never Before Green House Effects And Global Warming




Which Among The Following Is The Most Abundant Greenhouse Gas In The Earth S Atmosphere Answers
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived Greenhouse Gases Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide (CO 2) Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste, trees and other biological materials, and also as a result of certain chemical reactions (eg, manufacture of cement) Carbon dioxide is removed from theGreenhouse gas levels at new high Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the main driver of climate change, hit record highs last year and have continued climbing this




Global Warming And Greenhouse Gases Civilsdaily




Everything About Ipcc And Ipcc Report Ar6 21 Upsc Colorfull Notes
The UPSC Agriculture Optional Syllabus and Exam Pattern 21 has been released in the official notification issued by the Union Public Services Commission (UPSC) There will be three stages to the selection process of the candidates ie prelim exam, main exam and the interview stage Candidates must qualify the prelim exam to be eligible for the mains The main exam will The UK produces an annual greenhouse gas inventory, a consistent time series of UK greenhouse gas emissions from 1990 onwards Official statistics on UK greenhouse gas emissions are also producedThe IPCC also has a Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, whose main objective is to develop and refine a methodology for the calculation and reporting of national greenhouse gas emissions and removals The Working Groups and Task Force handle the preparation of reports, selecting and managing the experts that work on them as authors The activities of each Working




Upsc Prelims Answer Key Cut Off S Analysis Part 1 Iasbhai
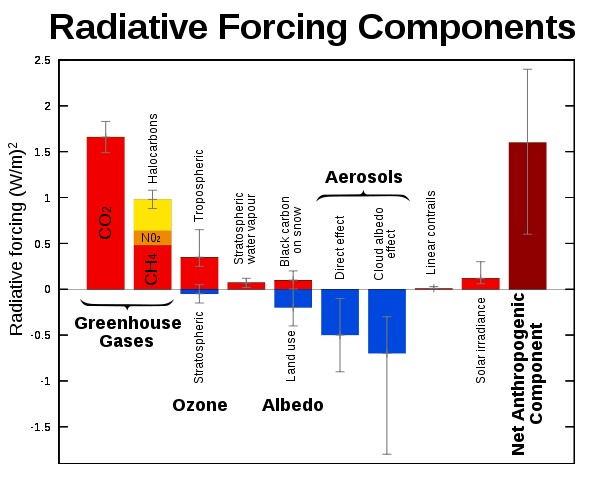



Climate Forcing Energy Education
Current Affairs Module (Prelims 21) Current Affairs Test Series (Prelims 21) Mains;The greenhouse gases trap heat in the earth's atmosphere and warm the planet This is an important topic in the environment and ecology section of the UPSC Syllabus What are Greenhouse Gases? UPSC examiner has accomplished that mostly by focusing on Contemporary Affairs that happened before 18, and ensure that it was from outside the routine preparation sources How to prepare Environment and biodiversity for Prelims – ?




Peatlands And Climate Change Iucn




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
Greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases are gas molecules that have the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases, and they have a




Greenhouse Gases Co2 Methane Nitrous Oxide Fluorinated Gases Water Vapour Their Sources Youtube




Is India On Track To Meet Its Paris Commitments




Wmo Greenhouse Gas Bulletin The State Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Based On Global Observations Through 19 No 15 23 November World Reliefweb



Global Warming




Emission Gap Report Insightsias







3




Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Iasmania Civil Services Preparation Online Upsc Ias Study Material




Name Any Two Greenhouse Gases Youtube
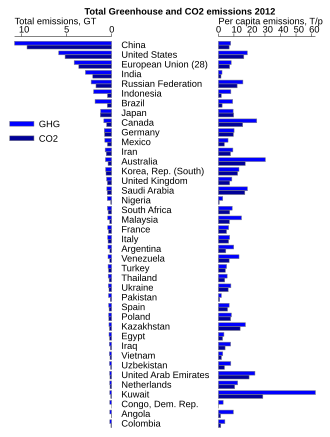



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



How Does A Upsc Personality Test Call Letter Look Like Quora
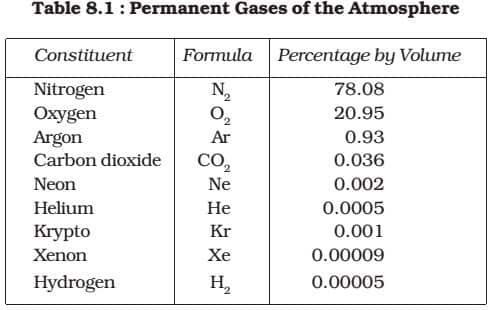



Composition And Structure Of The Atmosphere Geography Upsc
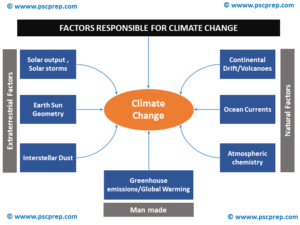



Climate Change And Summits Pscprep The Biggest Community Of Upsc Pcs Aspirants




List Of Green House Gases Ies Gs Environment And Energy Youtube




Ias Preparation Simplified Like Never Before Green House Effects And Global Warming




Green House Effects Global Warming Upsc Cse Ias 21 Ajit Tiwari Youtube




Climate Change Summits And Efforts Till Upsc Iasbhai



List Of Countries By Greenhouse Gas Emissions Per Person Wikipedia



1




Nitrogen Pollution Cause Effect In India Current Status Diademy




Global Warming And Greenhouse Gases Civilsdaily




List Of Green House Gases Ies Gs Environment And Energy Youtube




Upsc Cse Gs Greenhouse Effect Offered By Unacademy




L16 Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Achievers Batch Upsc Cse 21 Ajit Tiwari Youtube



Simple




Climate Change Causes Impacts On India World Upsc Ias Express




Sources And Sinks American Chemical Society
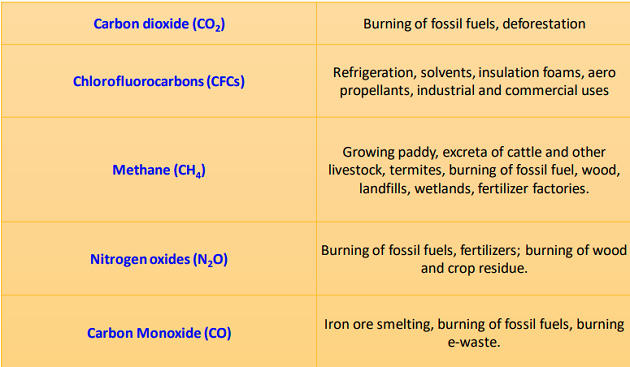



What Is Greenhouse Effect Burning Issues Free Pdf Download




Important Environmental Conventions Environment And Ecology Upsc Prelims 21 La Excellence Youtube
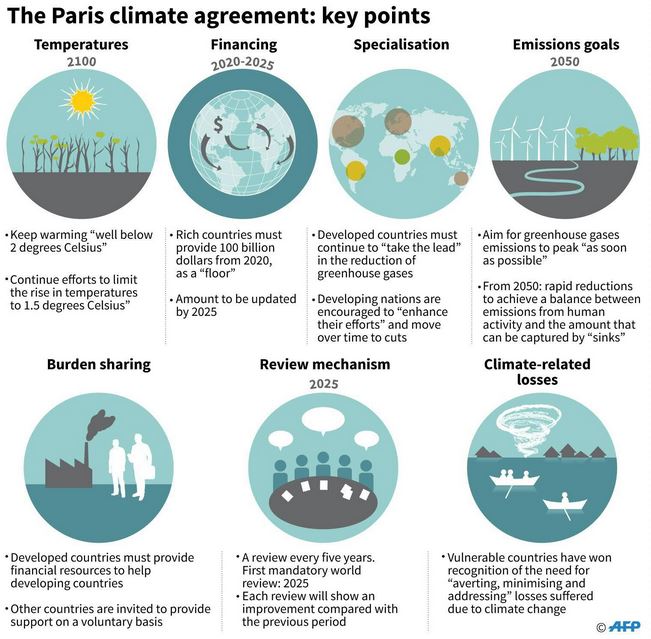



Five Years Of Paris Climate Accord Daily Current Affairs Abhipedia Powered By Abhimanu Ias




Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Iasmania Civil Services Preparation Online Upsc Ias Study Material




Climate Change And Land Ipcc S Report Drishti Ias
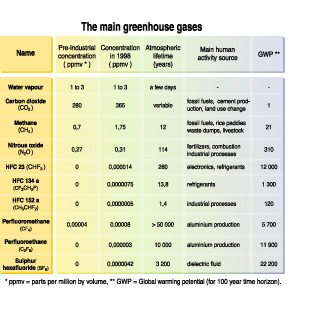



Main Greenhouse Gases Grid Arendal




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples




Climate Change And Land Ipcc S Report Drishti Ias




Green Hydrogen Upsc Iasbhai




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Factsheet India Global Climate Change




Climate Change Forumias Blog




Brain Booster For Upsc State Pcs Examination Topic The Lancet Countdown On Health And Climate Change Dhyeya Ias Best Upsc Ias Cse Online Coaching Best Upsc Coaching




Global Warming And Greenhouse Gases Civilsdaily
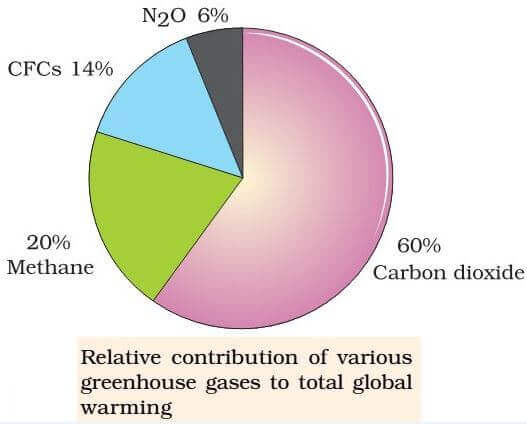



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias




Climate Change And Land Ipcc S Report Drishti Ias




Year End Review 19 Ministry Of Environment Forest And Climate Change




The Main Greenhouse Gases Source Is Prevent Air Pollution Download Scientific Diagram




Ipcc List Of Greenhouse Gases Wikipedia




Environment Climate Change And Global Warming One Liner Notes That You Should Not Miss India Shastra




Climate Change Performance Index




Upsc Prelims Answer Key Cut Off S Analysis Part 1 Iasbhai
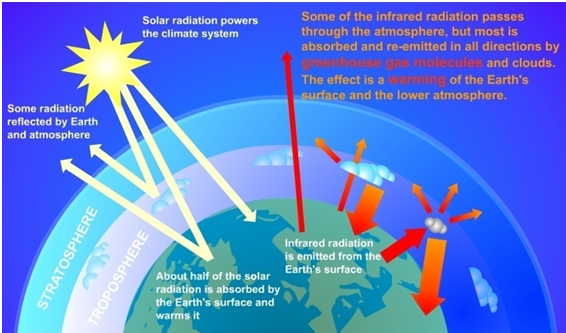



Green House Effect Gktoday




Un Climate Action Summit 19




Daily Current Affairs For Upsc Civil Services Exam 31 August 21 Argutes




Ozone Layer Formation Importance Depletion Effects Videos Examples




Blog Global Climate Change




Weakening Of Gulf Stream System Amoc Upsc Rauias
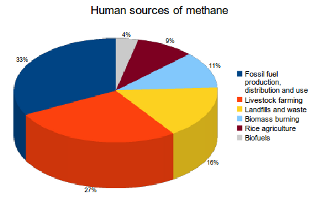



Main Sources Of Methane Emissions What S Your Impact




Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Secure Ias




E 3 2 List The Main Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources And Discuss Their Relative Effects Youtube




Upsc Cse Gs Greenhouse Gases Offered By Unacademy




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Carbon Sink Wikipedia




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples




7 Pm Impact Of Livestock On Climate Change 31 January 19 Forumias Blog




8 Upsc Prep Ideas Essay Tips Good Essay English Writing
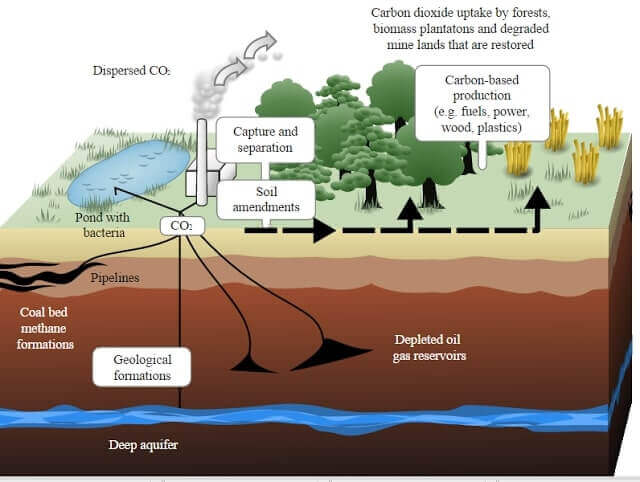



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias




Immediate Action Required An Open Letter To The Unfccc Secretariat Architecture 30




Carbon Footprint And Carbon Offsetting Aspirants Upsc Ssc Preparation
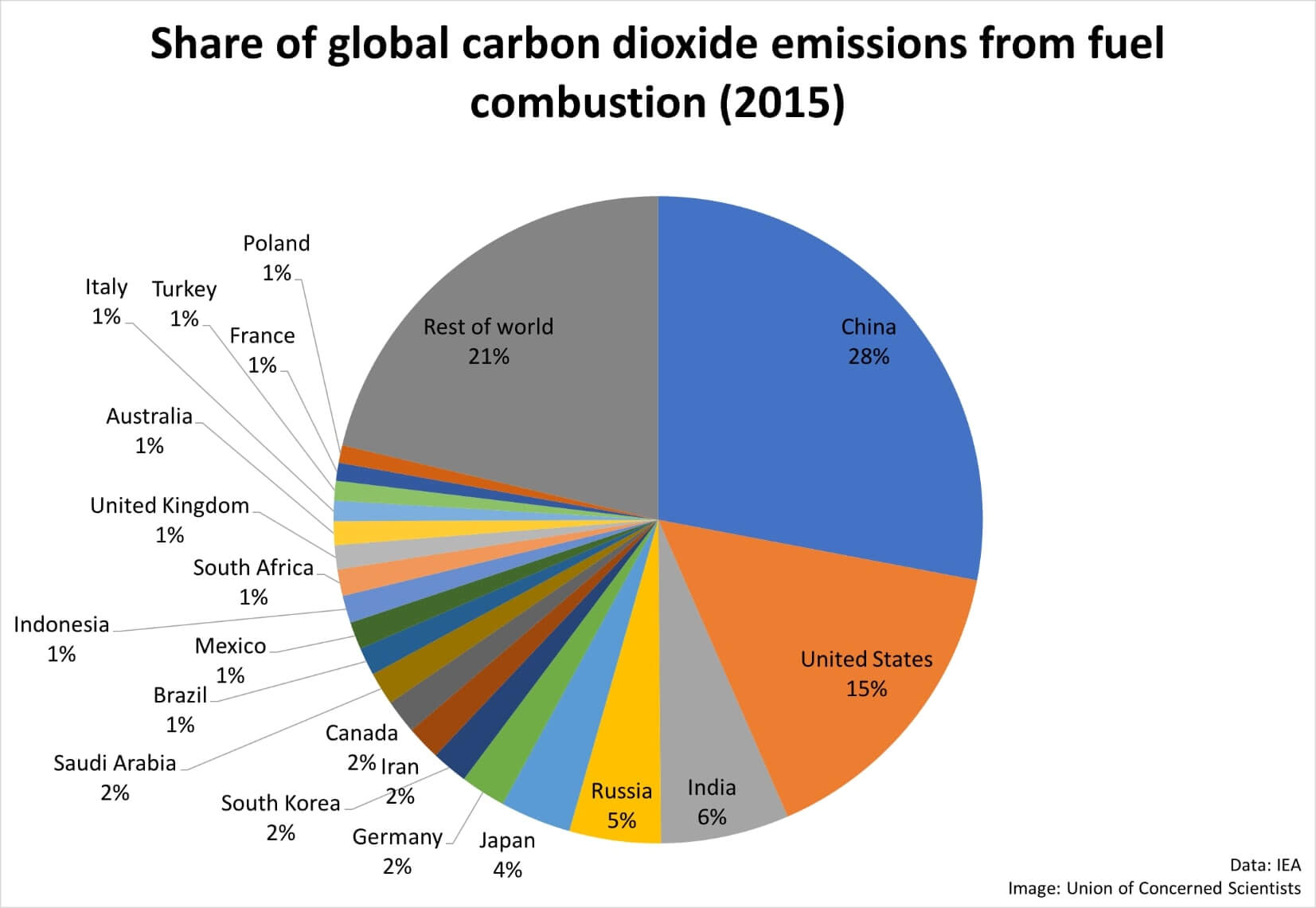



Unfccc Kyoto Protocol Unfccc Summit 1997 Carbon Trading Pmf Ias




Co2 Level Hit Record High



Dream Upsc Climate Change And Global Warming Introduction




Mcqs On Basic And Green House Gases 4 Crack Upsc Cse Ias Deepak Singh Youtube
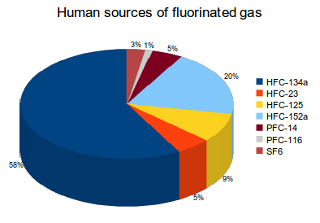



What Are High Global Warming Potential Gases What S Your Impact




Global Warming And Greenhouse Gases Civilsdaily
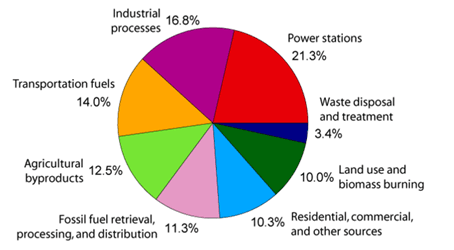



Greenhouse Gases Ghgs Gktoday




Environment And Ecology For Upsc Union Cabinet Approves Ratification Of Kigali Amendment To The Montreal Protocol On Substances That Deplete The Ozone Layer For Phase Down Of Hydrofluorocarbons Hfcs T Co Ijebbzhmqw




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects



Meet The Greenhouse Gases Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gas In Atmosphere Ias Gatewayy




United In Science Report Upsc Iasbhai




Carbon Footprint And Carbon Offsetting Aspirants Upsc Ssc Preparation




Pin By Upsc Pathshala On Upsc Exam Details Ias Books Geography Books
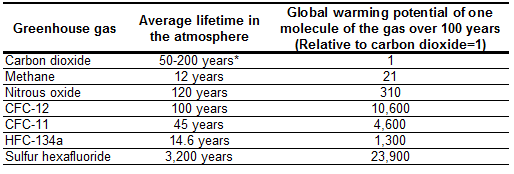



Role Of Ponds In Global Warming Current Affairs




Ocean Deoxygenation Iucn
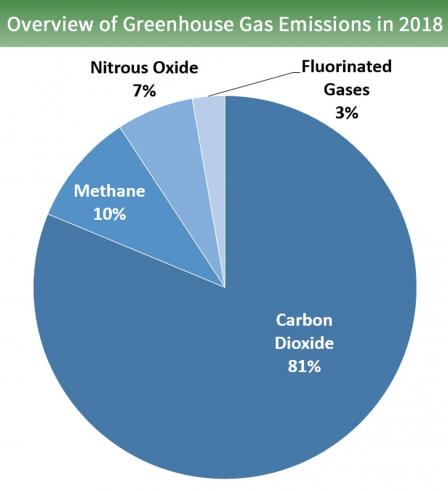



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Unit 4 Environmental Conventions Upsc Notes Life Of Ram



Greenhouse Gas In Atmosphere Ias Gatewayy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿